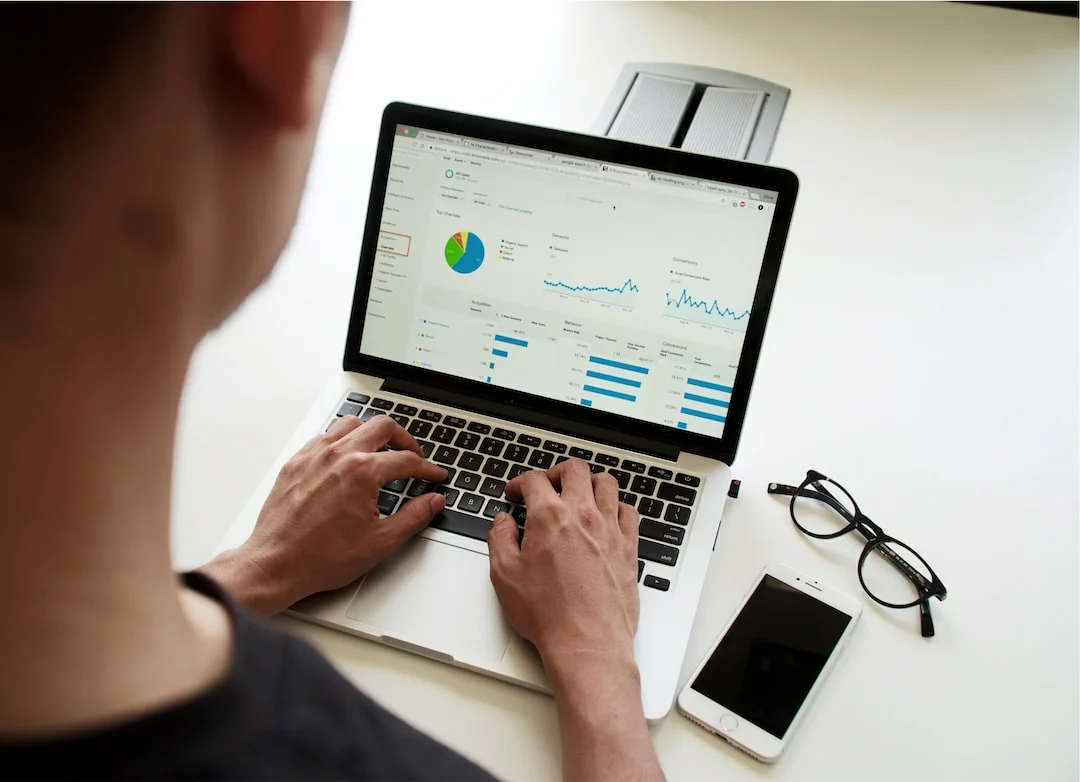
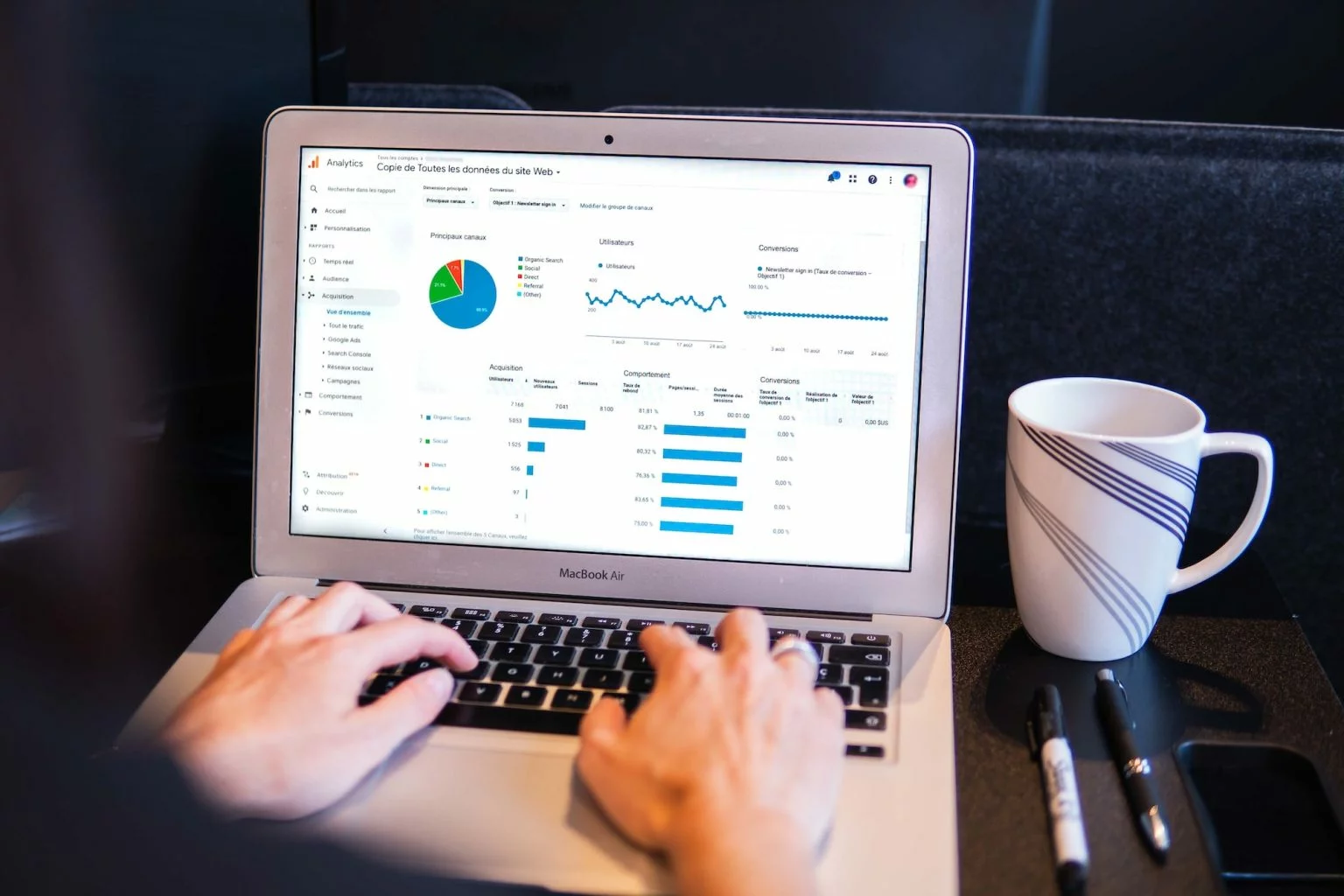
Configuring Google Analytics, a key step!
Google Analytics provides a wealth of information about your online presence. There’s just one condition: set up your analytics account properly beforehand.
Who wants to make decisions based on incomplete or inaccurate data? In this article, we take a step-by-step look at how to set up Google Analytics correctly.
Let’s start with the mistakes regularly made when setting up Google Analytics. Even if your business is unique for many reasons, you can start by following these tips, which apply to all sites, even yours 🙂
Also read: How to set up the Conversion Funnel in Google Analytics
1. Check that the tracking code is correct and complete
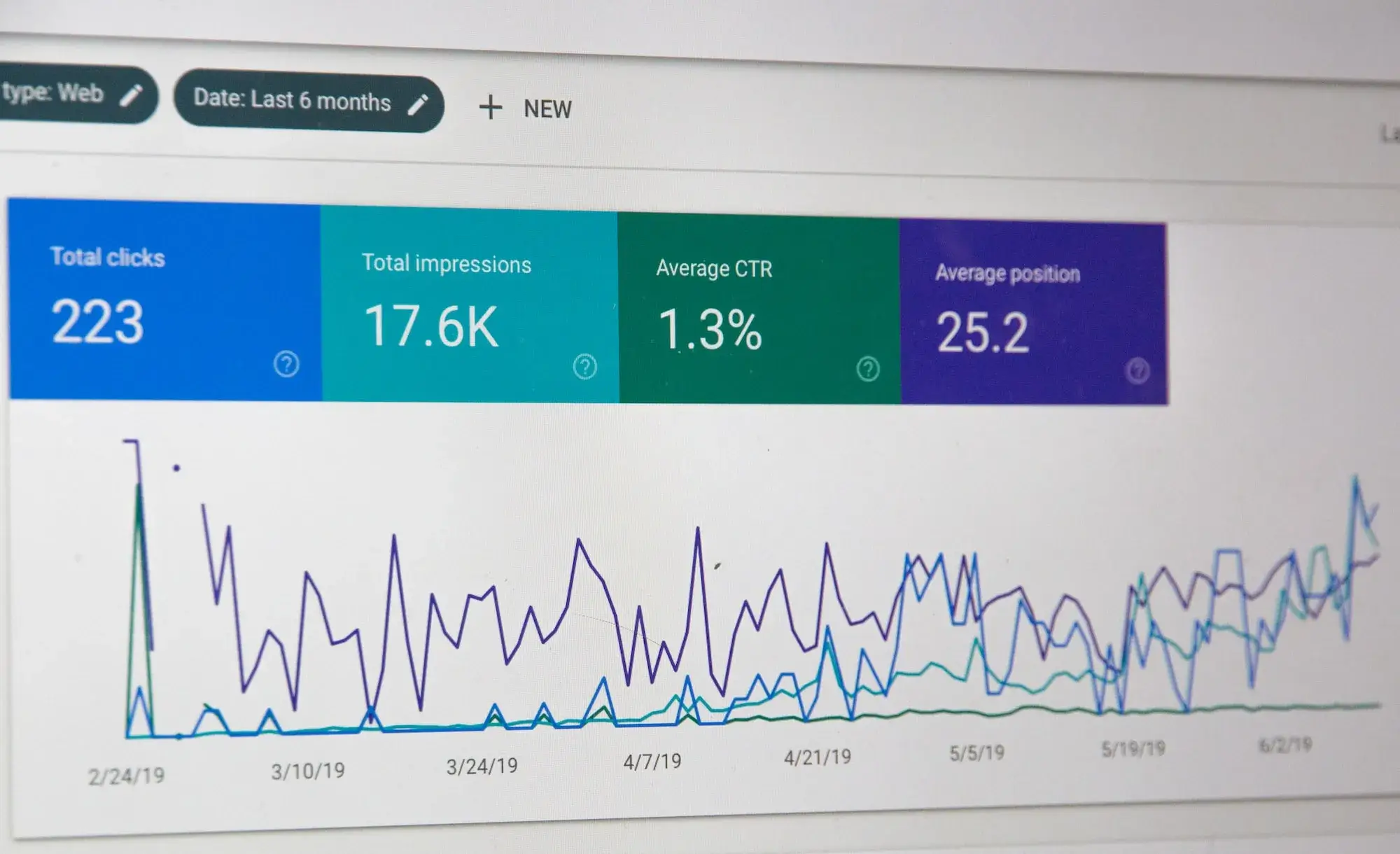
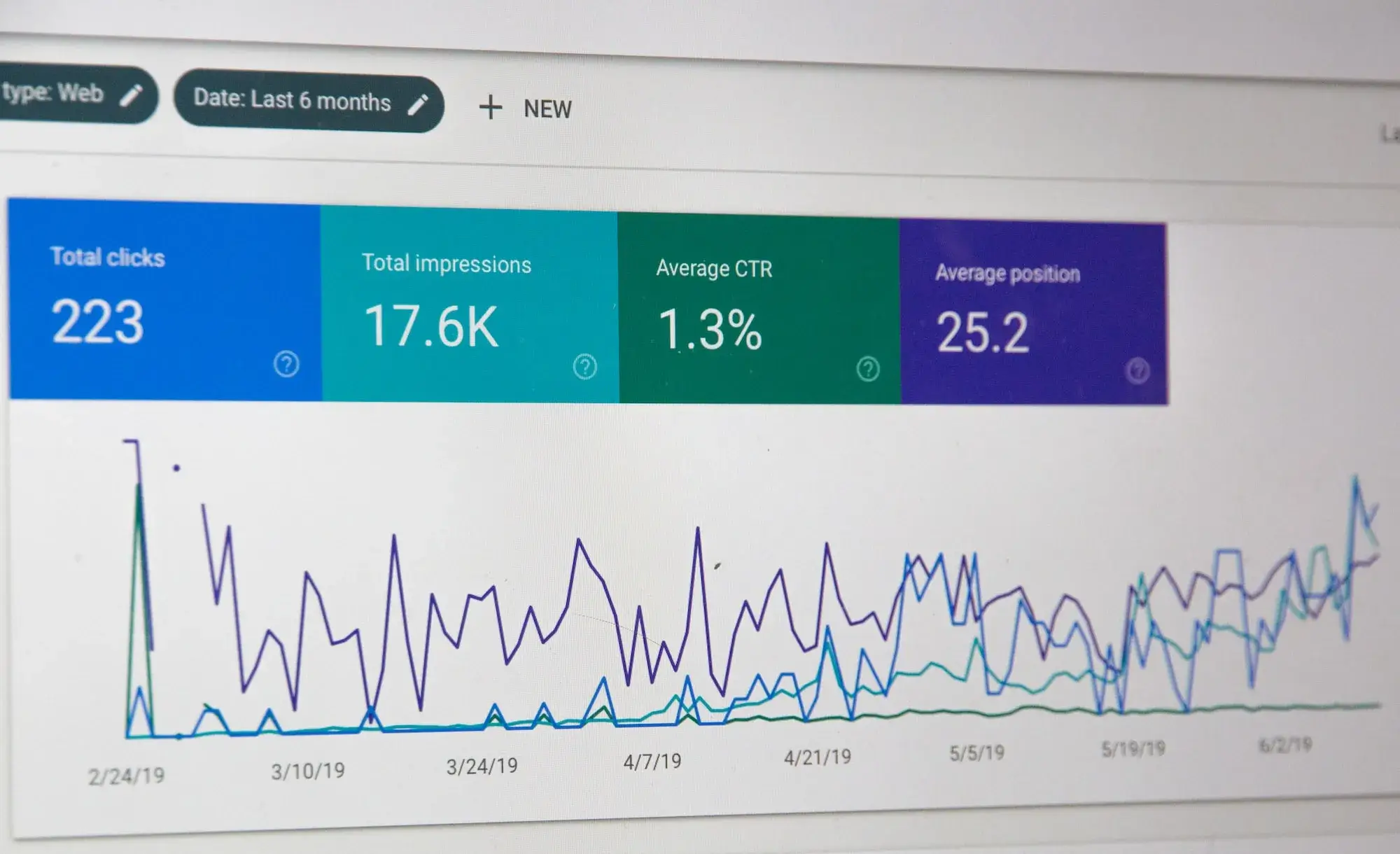
The tracking system is at the very top of the list of configurations that need to be set up correctly. Without it, you run the risk of missing out on key data on existing conversion stages on your site.
Tools for checking your configuration
There are various tools you can use to check your analytics configuration and make sure everything’s running smoothly.
Tag Assistant: perfect for checking configuration and resolving detailed problems at “page” level.
Tag Assistant is a Chrome extension that can be used to validate and diagnose your Google Analytics data on a page-by-page basis. Once you’ve solved a problem, you can return to Tag Assistant to check that your tags are working properly.
Screaming Frog SEO Spider: ideal for detecting site bugs across all pages. This tool is perfect for finding out whether your tracking code is correctly installed on all your pages.
There are two versions available: a FREE version, for websites up to 500 URLs, and a paid version, for more than 500 URLs.
Your tracking code
At the very least, you should check two things with regard to the tracking code installed
Tracking code version: if you haven’t already done so,
make sure you switch to Universal Analytics. Tag Assistant will display the
version you’re using and whether or not you need to migrate.
**Code location **: where to place your tracking code depends on whether you use Google Tag Manager or not.
It is increasingly recommended to use Google Tag Manager for tracking configuration.
Getting the code implementation right (according to your tagging plan) is a crucial step in getting reliable information from Google Analytics.
2. Setting objectives
Setting up Google Analytics objectives is a crucial step in data analysis. Without these objectives, you won’t be able to find out why your site is working or not, and where you can improve.
Objectives are generally based on form validations, downloads or purchase completion.
If your site is primarily dedicated to lead generation, it’s important to set your objectives on the form validation pages.
For e-commerce, conversions are essentially measured by the validation of a product sale. Tracking is specific to e-commerce.
It is obtained by integrating a few extra lines of code into your site.
In the article“How to set up your conversion funnel in Google Analytics“, we explain step-by-step how to create your own goals and conversion funnel in your Google Analytics account.
3. The backup "view
By default, Google Analytics lets you configure up to 100 accounts, 50 properties per account and 25 “views” per property. Multiple views are strongly recommended.
You should always configure a raw data view. Read this article if you’d like to know more about configuring different views in Google Analytics.
No matter how experienced you are, you need to have a backup view in place. Very often, there are several people working on the same Google Analytics account.
Make sure that NOBODY modifies the raw data view.